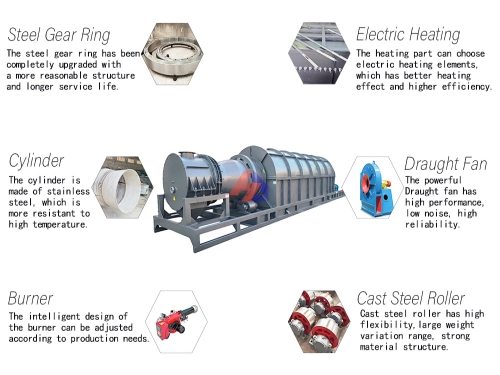
How Does an Activation Furnace Transform Carbonized Material into Activated Carbon?
The powerful adsorption capacity of activated carbon stems from its highly developed internal pore network. This network is not formed during the carbonization process, but is created in the subsequent activation step. This crucial transformation primarily relies on two technical pathways: physical activation and chemical activation. For modern production that prioritizes product purity and environmentally friendly operation, physical activation has become the more mainstream and reliable choice.
The Core of Physical Activation
The core of physical activation is the use of high-temperature steam or carbon dioxide as the activating medium. This process takes place in a specialized activation furnace.
In simple terms, when the carbonized material is heated to temperatures above 800°C, the introduced high-temperature steam undergoes a controlled oxidation reaction with the carbon atoms on the material's surface. This reaction selectively "burns away" the more disordered parts of the carbon structure and residual tars. As these carbon atoms are carried away in gaseous form, previously blocked micropores are opened up, and adjacent pores are connected. This creates a three-dimensional, interconnected, nanoscale pore network within the carbon.
The greatest advantage of physical activation is its purity and environmental friendliness. No chemical additives are used throughout the process, resulting in a final product free from residual impurities, with pure and stable quality. This makes it particularly suitable for producing activated carbon used in high-standard applications such as food, drinking water, and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, its exhaust gases consist primarily of combustible gases, which can be easily recovered and utilized to supply heat for the system, aligning with the requirements of clean production.
Why Is Physical Activation the Preferred Industrial Path?
In contrast, chemical activation, although used in laboratory or specific niche applications, shows significant disadvantages in large-scale industrial production, especially in scenarios with stringent requirements for product quality and environmental protection. This method requires impregnating the raw material with strong chemical agents such as phosphoric acid or zinc chloride. While it can create pores at lower temperatures, it inevitably introduces subsequent challenges like complex washing, wastewater treatment, and chemical agent recovery. This not only adds extra environmental burdens and costs but also carries an inherent risk of chemical residue, potentially compromising the safety and broad applicability of the final product.
Therefore, when evaluated from the perspectives of product purity, production environmental impact, long-term operational stability, and overall cost, physical activation based on high-temperature steam represents a more advanced and sustainable technological direction for modern activated carbon manufacturing. If you are also interested in producing activated carbon and wish to establish your own production line, you can contact Hengju Machinery.
About Hengju Machinery
Hengju Machinery is a technology-focused enterprise with years of research, development, and operation in the field of carbonization and activation furnaces. With our own production facility and a team of professional engineers, we are equipped to answer your various technical questions and provide high-quality furnace solutions.
Copyright: Copyright belongs to Hengju Machinery! Reprint please indicate the source: https://www.hengjumachinery.com/industry-news/how-does-an-activation-furnace-transform-carbonized-material-into-activated-carbon.html